Destruction of micro-organisms by heat
Pathogens are harmful microorganisms (bacteria) in food that can cause foodborne illnesses such as E coli and Salmonella. Sterilization and Pasteurization are thermal processes that cause the destruction these microorganisms by means of heat.
The safe inactivation of cells is caused by water being in close contact with proteins, such as the cell membrane of a bacterium. As the cell is heated water molecules vibrate quicker. This vibration causes the destruction of surrounding proteins to weaken and finally break their disulfide and hydrogen bonds. This alters the shape of the cell. The cell becomes denatured, preventing the proteins from functioning.
Water activity
The water activity of a product is a measurement for the dryness of a product ranging from 0 to 1. If there is free water available then the water activity is high, near 1.
The water activity is measured by defining with which humidity of air a product is in equilibrium.
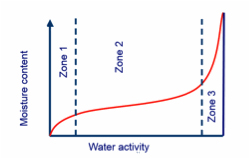
water activity graph
- Water activity is defined as the ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a material (p) to the vapor pressure of pure water (po) at the same temperature.
- The water activity (aw) represents the ratio of the water vapor pressure of the food to the water vapor pressure of pure water under the same conditions
- aw = p/po = ERH (%) / 100
- p = water vapor pressure at a certain temperature / pressure
- p0 = water vapor pressure of pure water at a certain temperature / pressure
Zone I
- Strongly absorbed water
- Water is not able to serve as solvent, behaves as part of the solid
- Monolayer (and less) water
Zone II
- Occupies the remaining layers around hydrophilic groups
- Multilayer water : associates with neighboring molecules by w-w / w-s / hydrogen bonding
- Decrease of chemical reaction rates
- Almost no growth of micro-organisms
Zone II
- Least strongly bound and most mobile water (molecularly)
- Available as solvent
- Allow most chemical reactions and microbial growth
- >95% of total water content for wet products!
At any given EMC (Equilibrium Moisture Content), aw increases with increasing temperature (product dependent factor).